What is Low-E glass?
2025-01-09
What is Low-E glass?
Low-E glass, also known as radiation coated glass, is a product in which one or more layers of metal or other compound films are coated on its surface. Low-E glass can be divided into online Low-E glass and offline Low-E glass according to the production process.
Their manufacturing processes are mainly divided into two types: online high-temperature pyrolysis deposition method and offline vacuum magnetron sputtering method. The former is completed in the cooling stage of the float glass production line, where liquid metal is directly sprayed onto the surface of the hot glass to form a film layer. This method produces Low-E glass with lower cost, but its thermal properties are not as good as the latter. The offline vacuum magnetron sputtering method is carried out in an independent device, using a multi-layer structure, including at least one functional layer with pure silver as the core, and a metal oxide layer for protection. The Low-E glass produced by this method has a higher energy-saving effect, but it needs to be made into insulating glass for use and is not suitable for long-distance transportation.
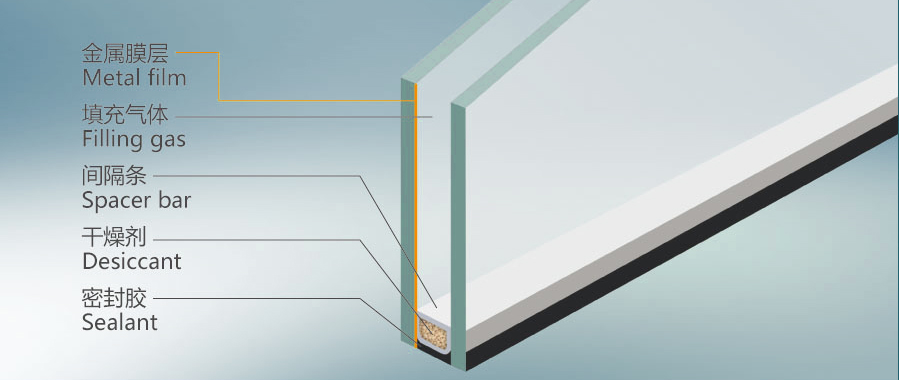
Due to the fact that online Low-E glass is directly produced on the production line, the color is relatively uniform and generally depends on the color of the original sheet. Offline Low-E glass is produced on different production lines, providing a wider range of visible light transmittance and infrared reflectance control, resulting in a more diverse range of color choices.
Online Low-E glass can be directly tempered, bent, and other processed. Its film layer is relatively stable and can maintain good performance even when exposed to the environment. It can be used alone without the need for hollow structure protection; On the contrary, offline Low-E glass must be made into composite products such as insulating glass to ensure long-term stability due to the fragility of the silver film; Due to this characteristic, the manufacturing cost of offline Low-E glass is higher than that of online Low-E glass. But offline Low-E glass, due to the use of silver film layer, has better thermal insulation performance, lower heat transfer coefficient, and lower shading coefficient, which makes it perform better in energy saving.
In terms of application, online Low-E glass is more suitable for ordinary residential projects or occasions with low color requirements. Offline Low-E glass is often used in high-end public and commercial buildings due to its superior performance and diverse appearance.
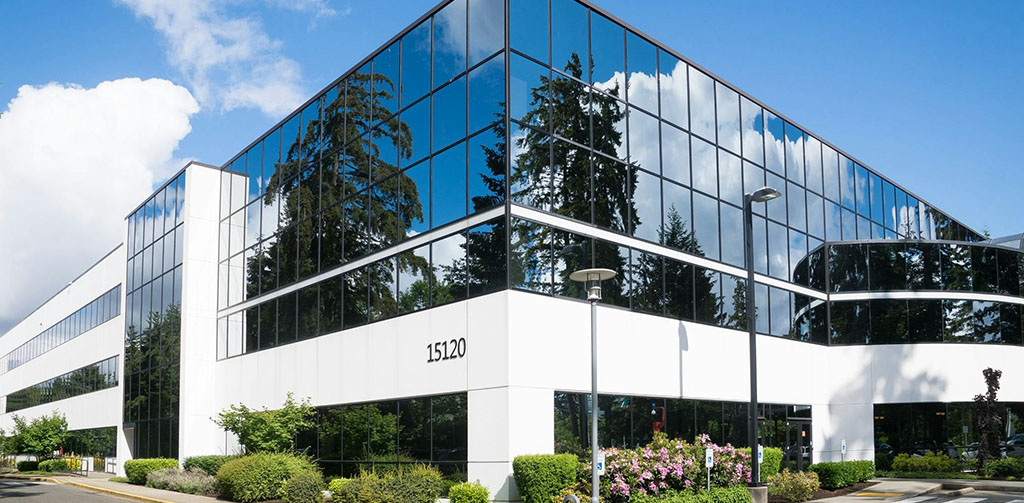

Low-E glass not only helps maintain indoor warmth and reduce heat loss in winter, but also blocks external heat from entering the room in summer, thereby reducing air conditioning load. Both types of Low-E glass have their specific applications, and when choosing, it is necessary to consider factors such as the specific needs of the project, budget constraints, and expected aesthetic effects.




